Concepts of System, Types of Systems, Surroundings
Concepts of System, Types of Systems, Surroundings: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, System in Thermodynamics, Surroundings in Thermodynamics, Boundary in Thermodynamics, Isolated System, Closed System, Open System, Homogeneous System & Heterogeneous System etc.
Important Questions on Concepts of System, Types of Systems, Surroundings
The content of a sealed steel tube containing liquid mercury, liquid ethyl alcohol, and a mixture of saturated vapours of the alcohol and mercury is an example for _____.
The heterogeneous system has the boundary.
Differentiate heterogeneous system from homogeneous system.
List out the examples for heterogeneous system.
What is heterogeneous system?
The mixture of carbon dioxide and water is known as _____.
The oil and water system is a homogeneous system.
Why don't the components in homogeneous system separated by physical methods?
Air is an example for homogeneous system. Justify.
What is homogeneous system?
In thermodynamics, a process is called reversible when.
Which of the following statements is true for an open system?
An isolated system is that system in which:
We could have chosen only the reactants as system then walls of the beakers will act as _____ ?
The wall that separates the system from the surroundings is called _____?
A system in thermodynamics refers to that part of universe in which observations are made and remaining universe constitutes the _____ ?
Establish a relationship between the surroundings, system and universe?
A closed system is that which?
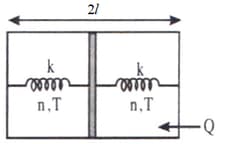
Determine the heat Q' given away to the thermostat by the left part of the piston if a horizontally insulated cylindrical vessel of length 2ℓ is separated by a thin insulating piston into two equal parts each of which contains n moles of an ideal monoatomic gas at temperature T and the left part is in contact with a thermostat (a device which maintains a constant temperature). Moreover, the piston is connected to the end faces of the vessel by undeformed springs of force constant k each.
System in which there is no exchange of matter, work or energy from surrounding is:
